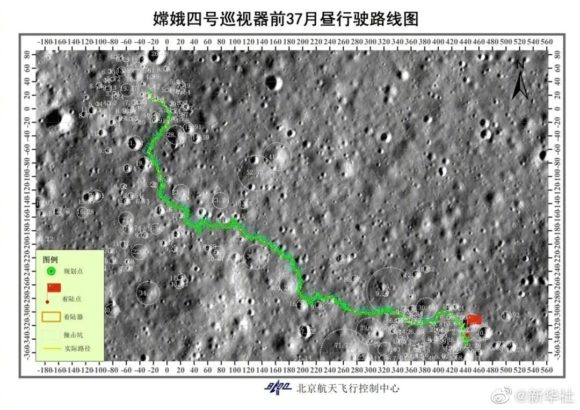
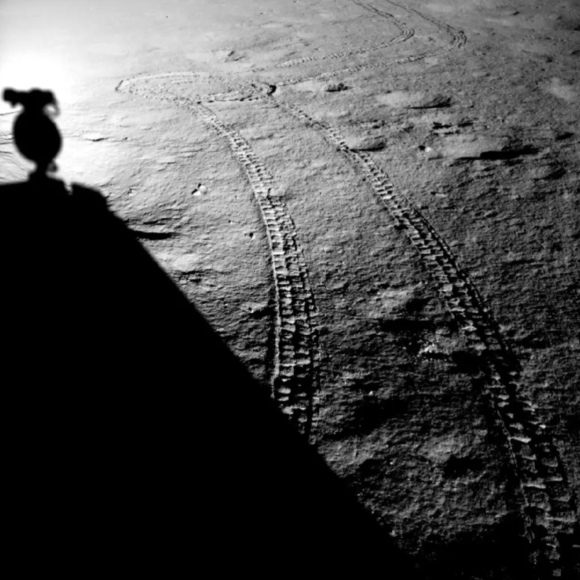
The Chinese probe Chang’e 4 became the first human artifact to gently land on the far side of the moon on January 3, 2019. About 12 hours after landing, the probe deployed the Yutu 2 rover, which, logically, also went down in history as the first to move along The far side of our satellite. Since then, three years have passed, and in this time, the little rover has been moving slowly but relentlessly. Recently, Yutu 2 (玉兔, “jade rabbit”) crossed the one kilometer mark on the lunar surface during the mission’s 38th lunar day. Specifically, on January 7, 2022, Yutu 2 reached 1003.9 meters. It’s certainly not an impressive number, especially when compared to the 10.5 kilometers traveled by Lunojod 1 or the more than 40 kilometers by Lunojod 2, but it’s not bad at all for a small 140 kg vehicle that can only operate during specific lunar periods (when The sun is not too low or high on the horizon to control that the temperature of the systems does not go out of parameters).

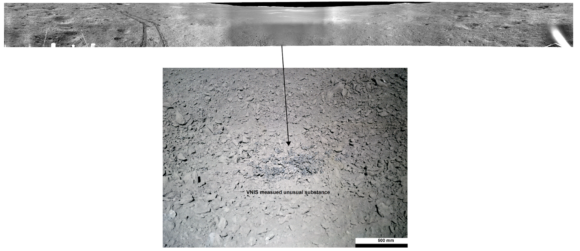
In any case, Yutu 2 has survived three years in a harsh lunar environment – it’s very difficult to keep a spacecraft operating 14 days in a row on a frigid moon night – a record it will surely hold for a long time, despite the new wave of lunar probes Planned for the next few years. During these 38 lunar days, Yutu 2 has continually moved away from Chang’e 4’s landing site to explore the Von Kármán crater. During this time, many articles have been published with Scientific results The rover’s mission and its photos circulated on the networks at times when it discovered something “unusual” on the moon’s surface. On the mission’s eighth lunar day (July 26-August 7, 2019), images of the crater were famous where a “jelly-like” substance was estimated. In fact, “gel” she was breccia-type rock fragmentsBrescia) measuring 52 x 16 cm, similar to those found by some Apollo missions, scattered across the crater floor.



On the 26th lunar day, early last year, Yutu 2 came across an unusual, pointed rock, which is appropriately called a “landmark” (里程碑). After analyzing it with the rover’s cameras and the VNIS instrument, the researchers concluded that it was likely a young rock that got there as a result of its impact not so long ago geologically. Between June and September 2021 – lunar day 31 and 34 – Yutu 2 passed through a series of craters on higher ground that were baptized by Mission Control “Turtle God” (神龟). Recently, Yutu 2 noticed a rock on the edge of a crater, and it is not clear why it was interpreted in the networks as a large “alien object”, hence the name “The Mysterious Compartment (神秘)”. Apart from the hottest interpretations of the images, The fact is that the lunar horizon, again, much closer and more accurate than the terrestrial horizon, played a trick on less experienced observers.During this 38th lunar day of the mission, Yutu 2 got a little closer to its target and verified that it was, in fact, a simple rock ( Although it is, yes, a shape much reminiscent of a hare, which is still a reference to the rover itself).





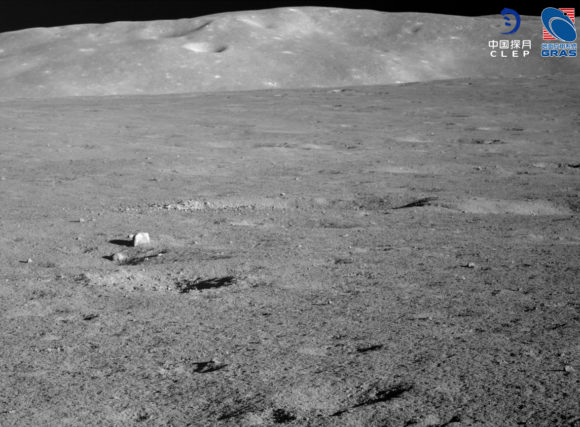
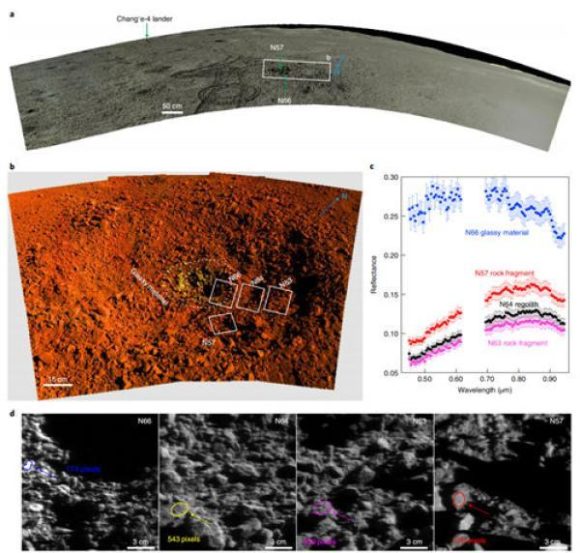
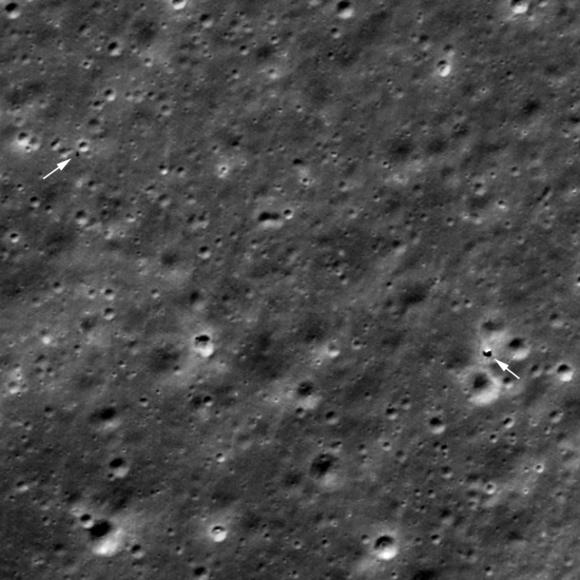
From a more official point of view, Yutu 2 has also been in the news recently thanks to article Published in Nature Astronomy, the probe team believes they have found fragments of a chondrite-type carbonaceous meteorite in and around the tiny crater that formed when it hit the moon’s surface about a million years ago. If this discovery is confirmed, this means that relatively volatiles-rich organic materials – including water – can be found on the Moon (water which it is worth emphasizing would not be the source of a manned mission, but it can help to explain where some of the reserves of this come from) Composite which can be observed today on the Moon). How could it be otherwise, meteorite fragments have been called “alien beings” in Chinese networks. Fragments of carbonaceous chondrites have already been discovered in rocks from the Apollo missions, but this is the first time they have been detected directly at the surface using remote instruments.
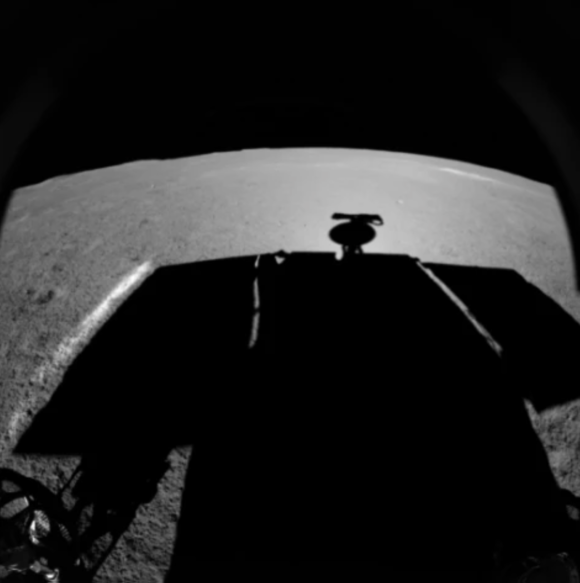




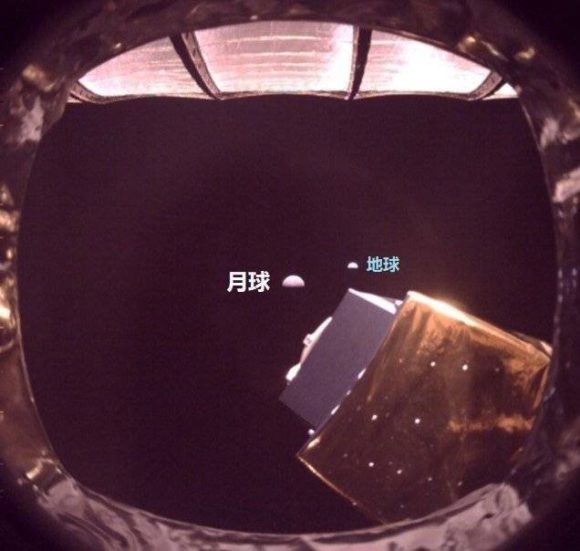
Yutu 2 adventure wouldn’t be possible without a satellite koekyaw, responsible for transmitting Yutu 2 and Chang’e 4 data from the far side of the Moon to Earth. Queqiao, launched on May 21, 2018, is the first satellite located at point L2 of the Earth-Moon system (EML2, not to be confused with point L2 in the Earth-Sun system) and the first satellite to use almost exclusively communications missions that are not at Earth’s orbit. Since May 2019, Queqiao has been transmitting Yutu 2 data directly to our planet. To stay at point L2, Kouquiao must adjust its orbit regularly. Following the success of the recent Chang’e 4 and 5 missions, China has confirmed that it will send the Chang’e 6, 7 and 8 probes – which make up the fourth phase of the China Lunar Exploration Program (CLEP) – to the south of the lunar pole. The probe will be launched first Chang’e 7, which will include elements from the Chang’e 3 and 4 missions, and in addition to Chang’e 5, Chang’e 6 will be launched later, similar to Chang’e 5, with the aim of bringing samples from the lunar side bunker. Finally, Chang’e 8 should be one of the first items in ILRS Automatic Moon Base China and Russia want to build on the south pole of our satellite.


References:
- http://www.chinanews.com.cn/gn/2022/01-07/9646793.shtml
- http://www.news.cn/2022-01/07/c_1128243103.htm
- http://www.chinanews.com.cn/gn/2021/12-01/9619811.shtml
- https://www.chinanews.com.cn/gn/2021/05-21/9482860.shtml
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0012821X20303228
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41550-021-01530-w
- https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202112/08/WS61b00da8a310cdd39bc7a058.html

“Beer enthusiast. Subtly charming alcohol junkie. Wannabe internet buff. Typical pop culture lover.”
