
After analyzing a group of fossil footprints discovered in La Rioja Province, northwestern Argentina, experts from Conisit Discover a variety of Little creatures Which They coexisted In an era dominated by… Large mammalsabout 15 million yearsduring the MyosinAn important stage of the Cenozoic era.
The research conducted after the discovery was published in the journal Journal of South American Geosciences. “The new findings reveal that Many species of mammals, birds and reptiles I coexisted in time and space, before The Great American Bio-ExchangeAn event occurred as a result of the physical proximity between the previously separate continents of North and South America. Moreover, that is Unique association of fossil footprints They are well recorded for that period: the Middle Miocene, 15 million years ago.
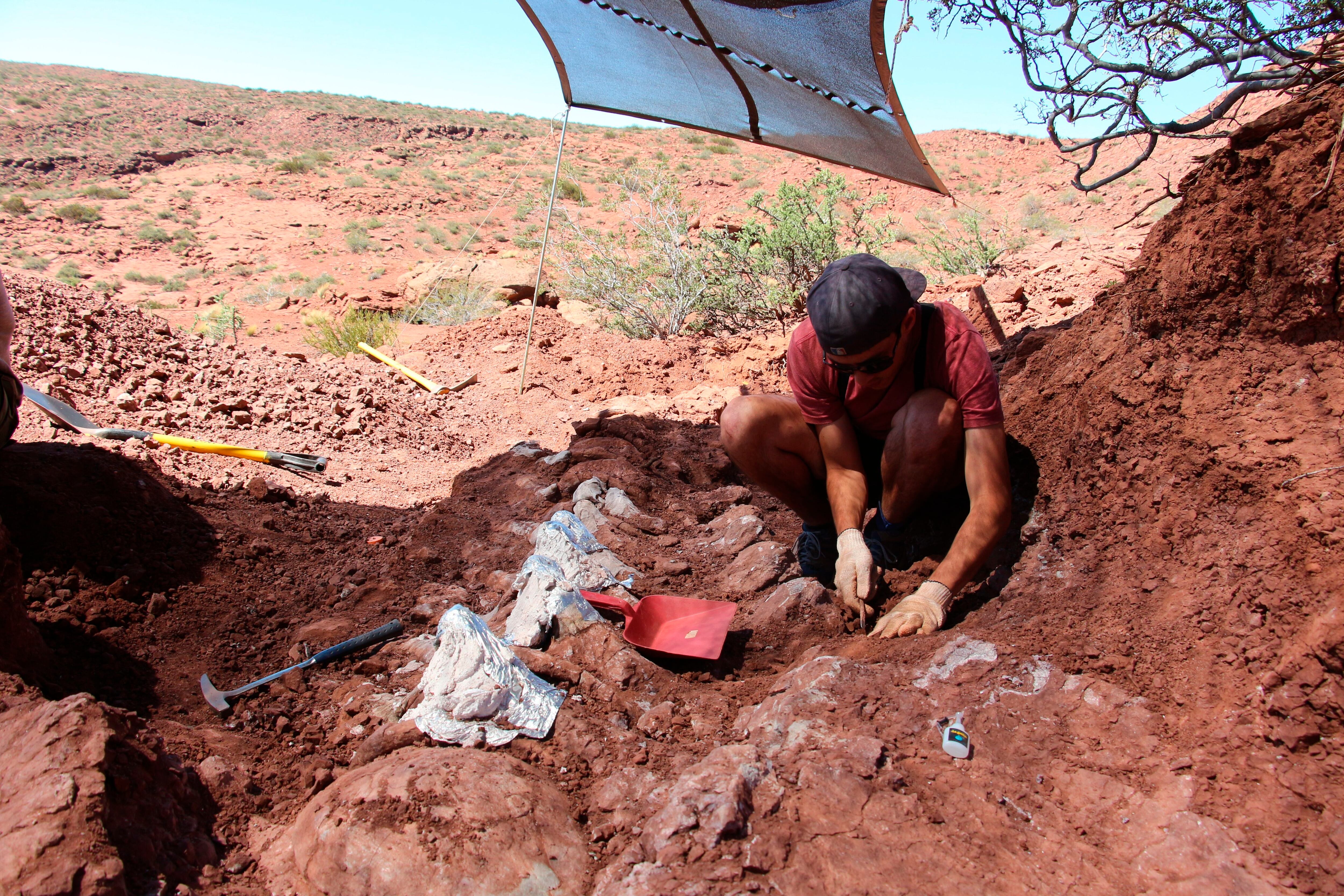
It all started in 2013, when geologists from… University of Buenos Aires (UBA) Discover a rock mass with fossil impressions nearby (Vincina in La Rioja).. Krabovicas, looking at photographs of the mass, was only initially identified Footprint of Tacheria Troiana. This footprint provided revealing insights into Large dinomid rodents, whose footprints have already been found elsewhere. However, this discovery provided more detailed impressions that provide information about their movement.
“From the photographs taken of the material, I was able to distinguish only one type of footprint from the total that we know today. It is related to Trojan TachiriaWhich was of revealing importance regarding the presence of large dynamid rodents whose footprints we had previously discovered in another area, but this new discovery shows More complete fingerprint patterns provide data on gait patternsKrabovicas explained. He highlighted: “Since then I wanted to go and inspect the area where that block came from.” However, for various reasons I was not able to go until 2022.”
That year with Rocio Vera and Martin Farina From his team, explore Krabovikas Pedregal Negro Gorge Near Vincina. This place is characterized by rocks dating back to the Miocene era, and despite the scarcity of bone remains, It is rich in well-preserved fossil footprints. “When exploring the area indicated by geologists, the surprise was immediate when we found Mass of fallen rocks And we realized that he showed a surface “full of little footprints”Krabovicas noted.
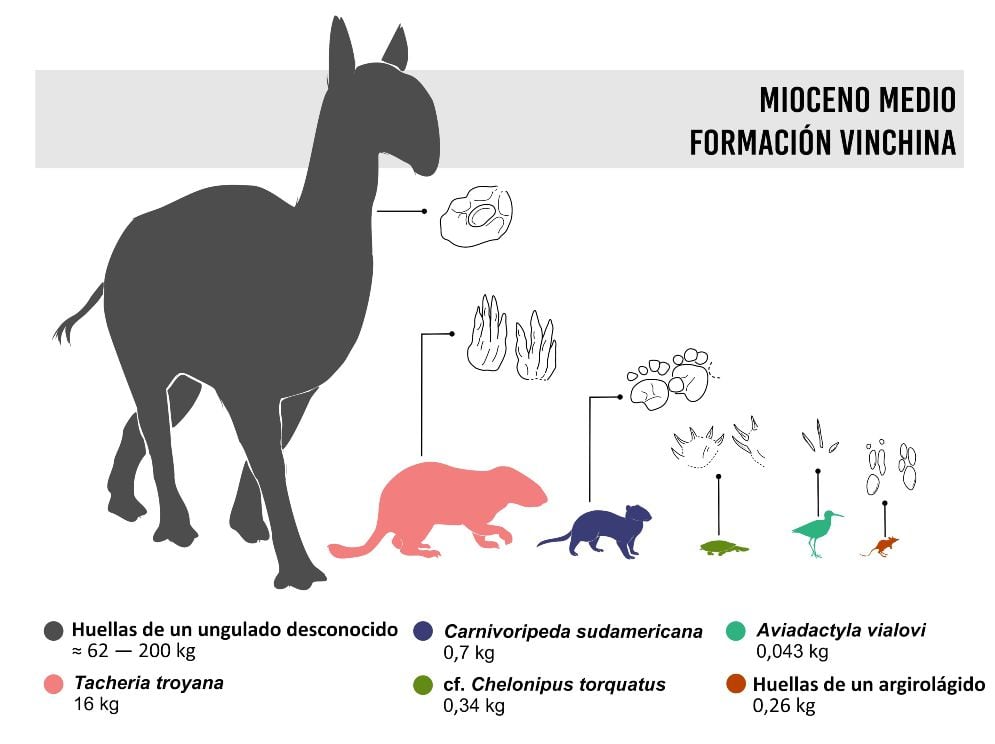
Previous research highlights the presence Large mammals that inhabited the area At that time, as well Macrocynchnus troyana, Related to the footprints of macrochnids about 130 kg, and Llastaya Yesera, roughly toxodontid footprints 75 kg, Both members of the distinguished band Extinct native ungulates of South America. However, his most recent research focuses on identifying which creatures are older and younger.

using 3D modeling techniques And based on Group accounts And body dimensions along with comparisons between Fossil bone remains and footprints of modern animalsThe research team discovered that the discovered group of footprints represents a community of… Small mammals, birds and turtles once inhabited the ancient river plains.
In these new animals, the most valuable item is the case south american carnivores, Footprints of small carnivorous mammals known as sparasodonts, with Short limbs and trunk about 20-25 cm long Of length And with A Weight not less than 1 kg. “These animals, which are completely extinct, share similarities with… Marsupials It is evolutionary related to iconography “Sabertooth” (Mammals with large fangs),” explained Rocío Vera, paleontology graduate student and CONICET doctoral fellow at IDEAN.
“We also discovered footprints arranged in pairs, which are the product of A Jumping bipedal gait of argyrolágid (Argyrolagiidae), a group of small, equally extinct domestic marsupials with a morphology similar to Gerbil Present (Diplopods) and the Kangaroo rats (Heterochromis), which represents an amazing example of evolutionary convergence,” explained Vera.

The investigation team also found traces of A Small freshwater turtle (Chelonibus torquatus) which – which Its length did not exceed 10 cm. “This discovery is important because continental turtle footprints are really rare in Cenozoic rocks,” said Martin Farina, paleontology graduate student and UBA PhD fellow at IDEAN.
Raised from the birds coastal (Aphiadactyla phialofi), l Giant rodents (Trojan Tachiria) related to pacaranas and footprints Extinct ungulates It was also preserved on the surface of the discovered stone block.
“In this work we present several fossil footprints Completely unknown to science to this day. On the one hand, it is the first and oldest evidence of the footprints of a completely extinct group of… Carnivorous mammals From South America: Sparasodonts. On the other hand, footsteps small extinct marsupials, known as “Argyrolagides”Krabovicas noted.
The researcher CONICET stated that the new findings Helping understand the fauna of South America in the Middle Miocene About the No knowledge is too perfectSince most of what is known comes from earlier (lower Miocene) and later (upper Miocene) associations. “There is also A beautiful interrelationship between modern and extinct animals. Animals that exist today help us understand what animals of the past looked like, and also show us what extinct animals looked like The dynamics of their societies across time and space And how different Climatic or environmental factors They could have influenced them, Krabovicas concluded.
Lucas Fernandez Piana, from University of San Andres, In the province of Buenos Aires; and Anne Colewyn, from the University’s Department of Artificial Intelligence in Biomedical Engineering Friedrich Alexander University Erlangen Nuremberg, In Erlangen, Germany.

“Beeraholic. Friend of animals everywhere. Evil web scholar. Zombie maven.”
