
The fact that we are experiencing a particularly hot period is largely due to our carbon dioxide emissions2and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere (global warming), during the interglacial period (geologically warm), It makes current conditions very different from those that prevailed during the ice ages.
However, you may be surprised to know We are living in an ice age, where the planet’s temperature is much lower than it would have been during warm periods that last much longer.occurred during the long history of the planet.
We usually talk interchangeably about ice ages, ice ages, ice ages, or ice ages, although the time scales for each of those cold periods that sometimes occurred on Earth are quite different. During Earth’s approximately 4.6 billion years, climate behavior has changed dramatically.; They alternated warm periods (much more so than today) with cold periods, during which a large part of the Earth’s surface was frozen.
Ice ages are cold periods shorter than ice ages, although these terms are incorrectly used synonymously.
In all, there were seven major ice ages, which we should not confuse with ice ages, which are much shorter cold periods.Which occurred during the Quaternary period. Which covers approximately the past 2.5 to 2 million years.
Milankovitch cycles
There is no single theory to explain why periodic glaciations, punctuated by periods between ice ages, begin to occur. The key was thought to lie in the increase in carbon dioxide concentration2 The atmosphere is linked to changes in ocean circulation, but recent studies point to changes in the Earth’s rotation axis that occurred at the beginning of the Quaternary era as a primary cause. These changes set in motion the observed dynamics, in which other changes also play their role.
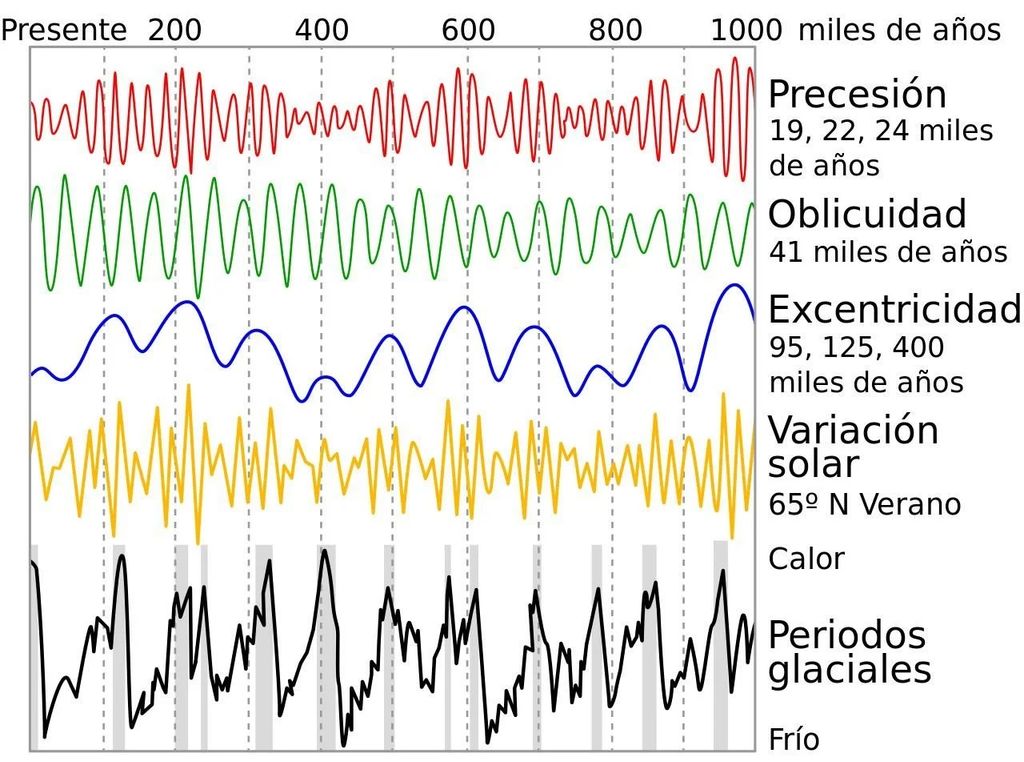
We cannot fail to mention Milankovitch astronomical theorywhich was developed nearly a century ago by the Serbian astrophysicist for whom it is named The appearance of glaciers is linked to certain configurations of three astronomical parameters of the EarthThis translates into less solar radiation reaching our planet.
These parameters are the difference in the eccentricity of the Earth’s orbitwith cycles of 100,000 and 400,000 years, the precession of the equinoxes, due to Changes in the tilt of the Earth’s axis of rotationwith a period of 22,000 years, What is known as a gestureIt is the slope of the axis of rotation, and its rotation period is about 4000 years.
The Earth will suffer from glaciers every 40 and 100 thousand years. These are caused by changes in their displacement according to the 3-variable Milankovitch cycle:
1️Eccentricity (var.aphelion perihelion) c/100 thousand years 2️Tilt: The axis varies from 21 degrees to 25 degrees c/41 thousand years 3️Precession: oscillating c/26 thousand years pic.twitter.com/vwiEt67HVr– El Tiempo +51 (@ClimaPeruMundo) December 26, 2022
Despite the elegance of this theory and the great support it has received,… The Earth is a complex system, in which the internal processes that occur within it can in turn cascade a series of changes that also affect the climate.So Milankovitch cycles alone are unable to explain all these differences, hence the factors mentioned above, such as tangential changes in the Earth’s rotation axis, CO2 Air or sea currents can become the main modulator of climate changes.
What was the last ice age? When will be next?
The last ice age is called the Würm in Europe And Wisconsin in America. It began a little over 100,000 years ago.When Neanderthals appeared in Europe, It ended about 12,000 years ago. During the approximately 90,000 years it lasted, there were different phases, all characterized by cold, although some were more severe.
The glacial maximum was reached about 20,500 years ago. Then the ice sheet reached its maximum extent., covering almost the entire British Isles. It is the time when our ancestors, the Cro-Magnians, took refuge in caves.
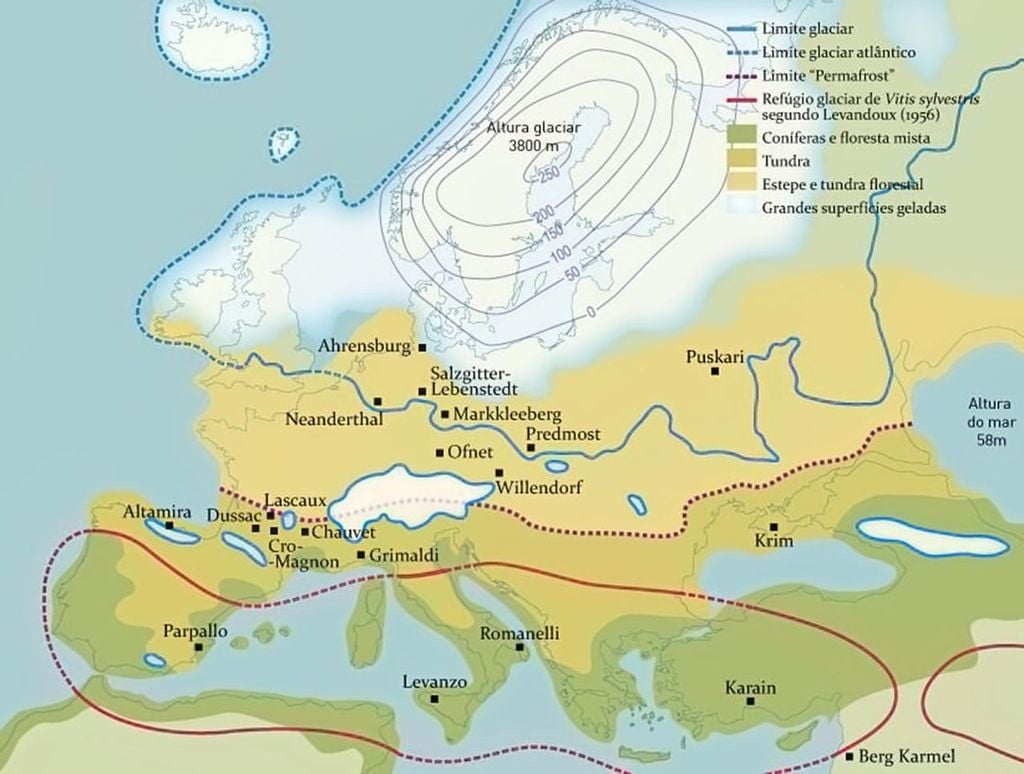
Little by little, this ice retreated northward, gaining space in green and forested areas.Which encouraged the development of hunting, agriculture, human expansion, and established the first civilizations.
From the Huronic Ice Age, which began more than two billion years ago, until the current Quaternary Ice Age, the Earth has gone through many cycles. These ice ages, driven by factors such as Earth’s orbital fluctuations and axial tilt, shape the landscapes and climates we see today. #Land pic.twitter.com/otoe5aT2kR
-Will Todd (@SubjectsPro) October 21, 2023
This glaciation was the last in a long list of glaciations that occurred on Earth during the aforementioned Quaternary period., separated – as we noted earlier – by warmer periods (between ice ages) of shorter duration. The end of this ice age marked the end of the Pleistocene and the beginning of the Holocene. Current geological era.
According to Milankovitch’s astronomical theory, sooner or later, we will have a new ice age on Earth. What is unknown is when this change will occur, and whether large-scale global warming can fully or partially counteract this return to extreme cold.
Taking into account the duration of the current Holocene and other previous glacial periods, we can think of no more than 1,500 years for the start of this new ice age; However, there is no shortage of scholars who posit this To continue increasing the carbon dioxide concentration2 In the atmosphere at the current rate or Mays, The next ice age could be delayed by tens of thousands of years. There are too many uncertainties that do not allow us to make predictions in this sense.

“Beeraholic. Friend of animals everywhere. Evil web scholar. Zombie maven.”
